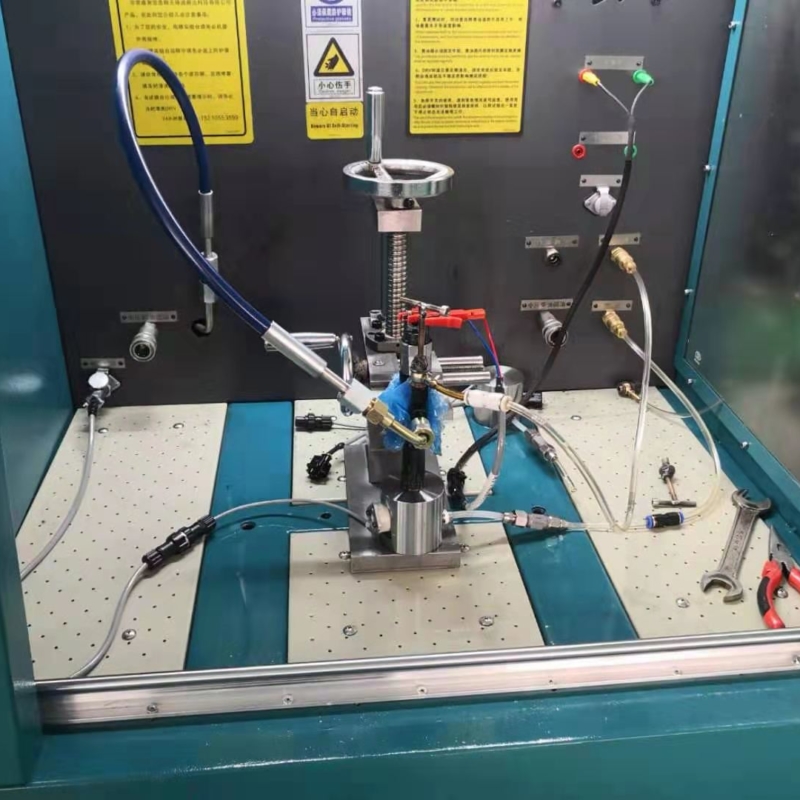
How To Repair The Common Rail Injector By Using Adjusting Shims? – Stage 3 Repair Solution.
The video is a demstration of stage 3 repair skill:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lgfn2meNmPw
Firstly we introduce the different working conditions of the common rail injectors:
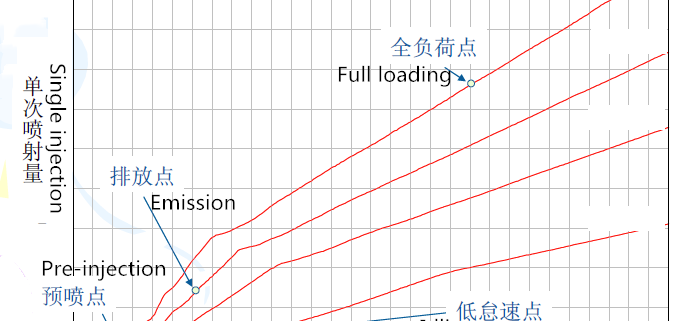
1) Full loading diesel fuel return: long power-on time, maximum rail pressure, fuel return, judge common rail injector sealing, whether there is enough diesel fuel supply capacity.
2) Full load fuel injection: long power-on time, maximum rail pressure, fuel injection quantity, determine the maximum fuel injection capacity of the common rail injector
3) Emission injection quantity: medium power-on time, medium rail pressure, fuel injection quantity, medium load determination, acceleration characteristic diesel fuel quantity of the common rail injector
4) Pre-injection quantity: short power-on time, medium-high rail pressure, fuel injection quantity, judge injector’s response ability, eliminate noise of the diesel injectors
5) Low idle injection quantity: long power-on time, low rail pressure, fuel injection quantity, judge whether the starting and idle diesel quantity is qualified
a) Foreword: All shims inside the common rail injectors, if in contact with the spring, directly affect the spring force; if contact with other parts directly affects the fit clearance or stroke between the parts.
b) Intermediate shims (needle valve stroke)
When the adjusting shims is thickened, the stroke of the nozzle is correspondingly reduced, which is equivalent to the smaller opening of the nozzle, and the flow rate of the long power-on time is most affected (including the total load).
c) armature stroke shims
The shims is thickened, the corresponding position of the solenoid valve is increased, the lift of the armature is increased, and the amount of diesel fuel is increased accordingly, which affects the fuel quantity of all test points, and the test point of the short energization time is particularly obvious.
d) Buffer stroke gasket (overlift shims)
The gasket is thicker and the over-lifting is smaller. The gasket has no significant effect on the fuel quantity, but the excessively thick gasket may cause the armature core to not fall, which may affect the valve ball seal, and vice versa. .
e) Grease spring adjusting shims.
The gasket is thickened and the spring force of the nozzle spring becomes larger. Under the condition of lower rail pressure, the needle valve is more difficult to open and the diesel quantity becomes smaller. When the rail pressure is higher, the spring force is much smaller than the upward force of the needle valve, and the influence can be neglected. Therefore, at low idle points, the diesel quantity has an obvious influence.
f) Solenoid valve spring adjusting shims
The shims is thickened, the spring force of the solenoid valve becomes larger, the armature response is more difficult, the response speed becomes slower, the diesel fuel quantity becomes smaller, and the fuel quantity at the discharge point is mostly affected.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!